Le bâtiment
À sa création, l'Ircam était entièrement souterrain, situé sous l'actuelle fontaine Niki de Saint-Phalle et Jean Tinguely de la place Igor-Stravinsky. Puis la tour de Renzo Piano a émergé en 1990 à l'angle de la Piazza, marquant l'inscription de l'Ircam dans le paysage urbain. Depuis 1996, l'institut arbore une façade horizontale hybride, constituée de deux autres volumes contigus à la tour, aussi disparates qu'une ancienne école Jules-Ferry et un bâtiment de Bains-Douches.
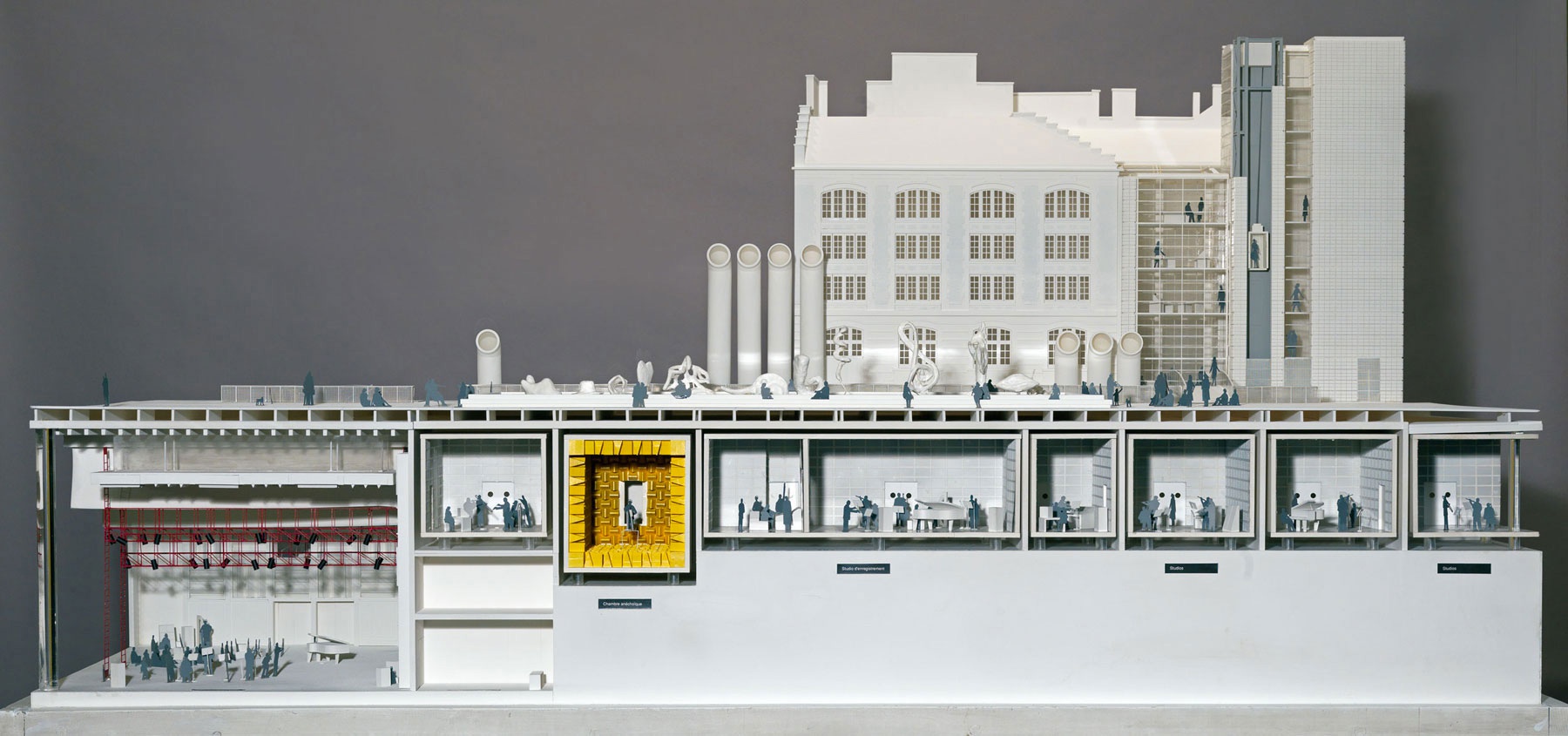
| Sous-sol (3500 m2) | Bâtiments Jules-Ferry et Bains-Douches (1969 m2) | Tour Piano (728 m2) |
| par Renzo Piano et Richard Rogers | par Daniel Rubin et Patrick Rubin | par Renzo Piano |
| en octobre 1978 | en 1996 | en juin 1990 |
| studios, laboratoires, Espace de projection, chambre anéchoïque, atelier mécanique | salle de conférences, médiathèque, salles de cours, bureaux | bureaux |
 Studio 1 © Laurent Ardhuin
Studio 1 © Laurent Ardhuin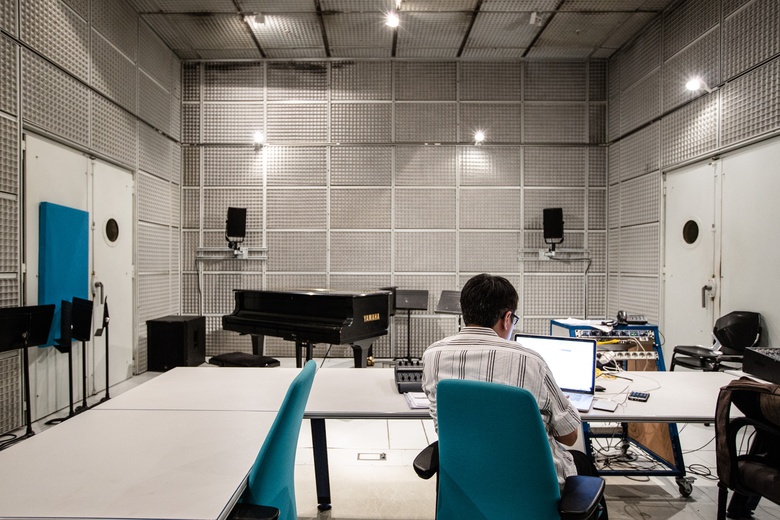 Studio à l'Ircam © Philippe Barbosa
Studio à l'Ircam © Philippe Barbosa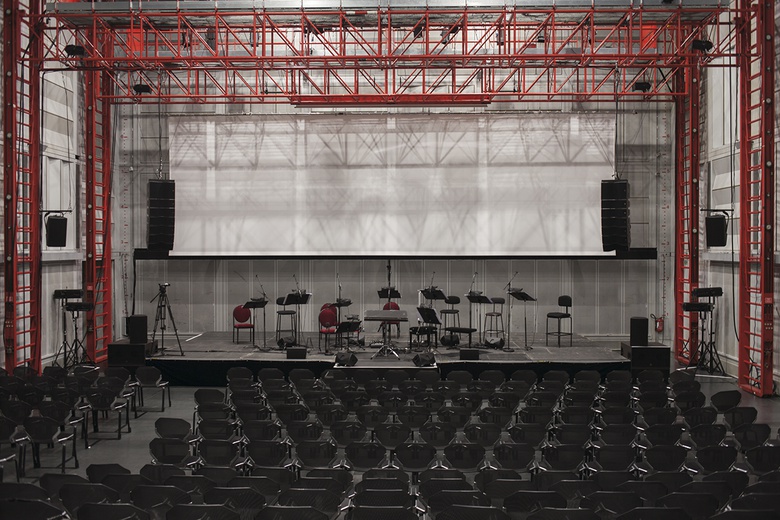 L'Espace de projection © Éric Laforgue
L'Espace de projection © Éric Laforgue L'Espace de projection © Éric Laforgue
L'Espace de projection © Éric Laforgue
Espace de projection (« Espro »)
L'Espace de projection est une salle à acoustique variable qui peut indifféremment s'utiliser comme salle de concerts, studio d'enregistrement et lieu d'expérimentations acoustiques. Ce volume est une boîte étanche, structure indépendante de la structure primaire de l'ensemble du bâtiment, ainsi isolée des bruits et des vibrations de l'extérieur. Plus vaste espace de l'Ircam, c'est le point culminant de tout le bâtiment.
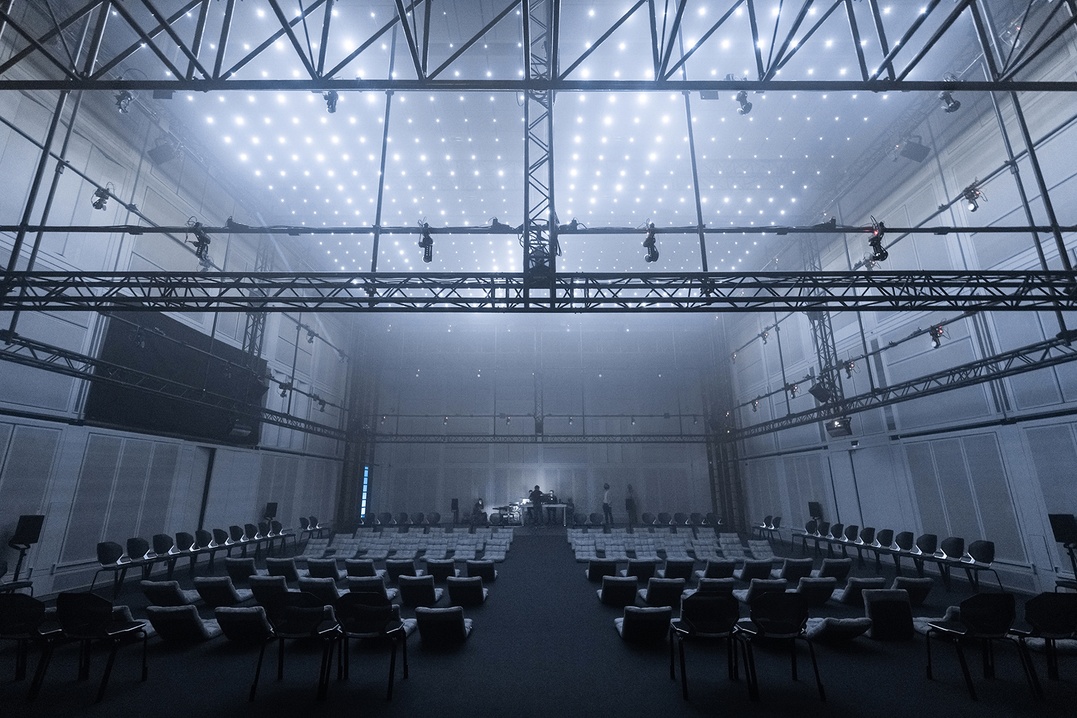 Espace de projection, Polytopes dans le cadre du festival ManiFeste-2022 © Ircam - Centre Pompidou, photo : Quentin Chevrier
Espace de projection, Polytopes dans le cadre du festival ManiFeste-2022 © Ircam - Centre Pompidou, photo : Quentin Chevrier
Équipement audio : un ambitieux système de spatialisation sonore multicanal
À la fois outil et objet de recherche, l’équipement audio de l’Espro combine deux systèmes de pointe en matière de reproduction du champ sonore, la WFS (synthèse d’hologrammes sonores) et Ambisonics (immersion sonore 3D). Le dispositif est constitué d’une ceinture de 264 haut-parleurs régulièrement répartis autour de la scène et du public pour la diffusion en WFS et d’un dôme de 75 haut- parleurs pour une diffusion tri-dimensionnelle en Ambisonics. Ces 339 haut-parleurs sont contrôlés par un ensemble d’ordinateurs gérant en temps réel la spatialisation des sources sonores.
Cet équipement a bénéficié du soutien financier de la région Ile-de-France (programme d’équipement Sesame), du CNRS et de Sorbonne Université.
 Acoustique variable
Acoustique variable
L'acoustique variable exige des parois et plafonds mobiles. Ainsi varient d'une part la position des plafonds et, de ce fait, la volumétrie de la salle, d'autre part, les matériaux des parois et des plafonds. Ces matériaux sont composés de modules prismatiques à trois faces (absorbante, réfléchissante et diffusante) appelés périactes. Ceux-ci sont regroupés par trois (171 groupes), et commandés par un système électromécanique.
Principales caractéristiques
Dimensions horizontales : 24m x 15,50m
Capacité d'accueil : 250 à 350 places
Variabilité du volume : hauteur du plafond entre 1,50m et 10,50m
Variabilité des caractéristiques acoustiques : temps de réverbation entre 0,4 et 4 secondes.
Acousticien : M. Peutz. Inauguration : octobre 1978
Chambre anéchoïque (« Chambre sourde »)
 Une chambre anéchoïque est une salle d'expérimentation dénuée d'effets de salle. Tous les matériaux (plafond, sol, murs) y sont absorbants. Des dièdres de laine de verre disposés sur toutes les parois permettent une absorption quasi-totale des ondes sonores émises. Ce type de chambre permet de recréer artificiellement des conditions dites de « champ libre » : le son s'y propage sans réflexion.
Une chambre anéchoïque est une salle d'expérimentation dénuée d'effets de salle. Tous les matériaux (plafond, sol, murs) y sont absorbants. Des dièdres de laine de verre disposés sur toutes les parois permettent une absorption quasi-totale des ondes sonores émises. Ce type de chambre permet de recréer artificiellement des conditions dites de « champ libre » : le son s'y propage sans réflexion.
Fonctions principales
La chambre anéchoïque sert principalement à faire des mesures de rayonnement de source. Une source sonore est un champ acoustique rayonné, très complexe à mesurer. Si l'on prend le cas d'un instrument de musique, son champ acoustique rayonné va dépendre de la note jouée, du type d'instruments, etc. Pour le mesurer, il est indispensable d'être dans une situation « anéchoïque », condition sans laquelle on mesurerait à la fois le champ direct rayonné par l'instrument mais aussi le champ réfléchi par toutes les parois de la salle. La chambre anéchoïque sert aussi de chambre « calme ». Des mesures de sons très précises nécessitent des niveaux d'enregistrement très faibles, sans bruit de fond. Très bien isolée de l'extérieur et du reste du bâtiment (sorte de « boîte dans une boîte », montée sur des silentblocs en néoprène), cette chambre permet d'avoir un rapport signal/bruit satisfaisant.
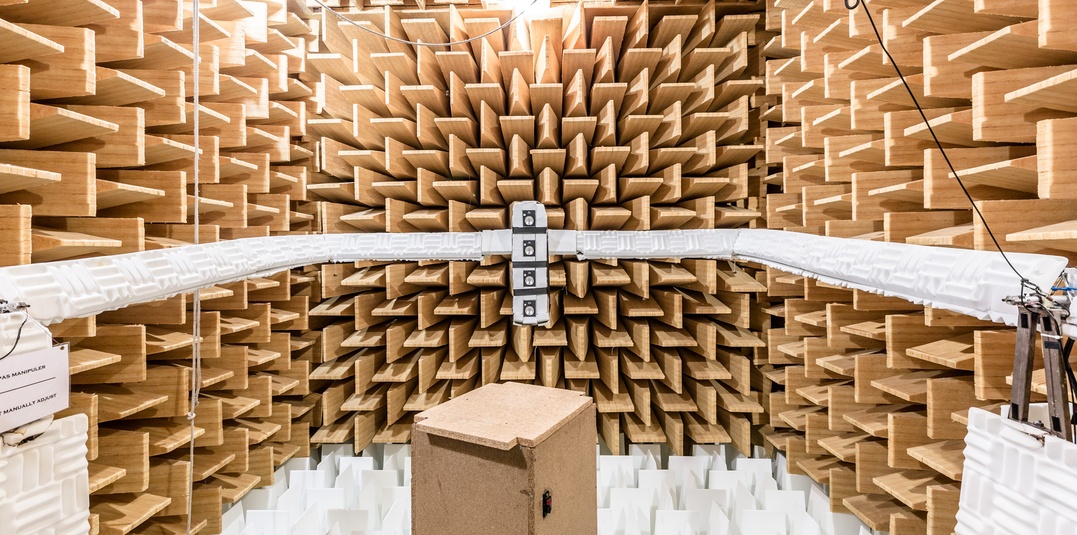

Photo 1 : Entrée de la chambre anéchoïque © Ircam - Centre Pompidou, photo : Cyril Fresillon
Photo 2 : Chambre anéchoïque © Ircam - Centre Pompidou, photo : Philippe Barbosa
Salle Stravinsky
Salle de conférence de 75m2 équipée d'un système audio, vidéo, projecteur et d'un accès au réseau Internet.
Principales caractéristiques
Estrade : 21m2. Capacité d'accueil : 7 rangs de fauteuils. 73 sièges fixes.
Location
Renseignements auprès du département de la Production
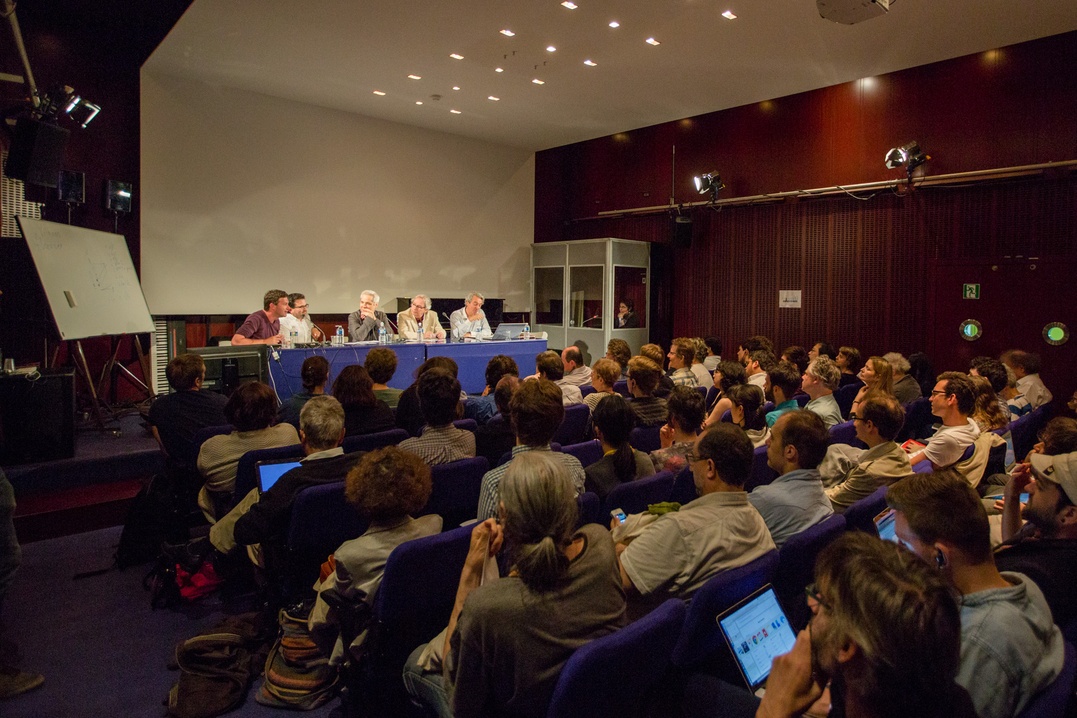 Salle Stravinsky © Ircam - Centre Pompidou, photo : Philippe Barbosa
Salle Stravinsky © Ircam - Centre Pompidou, photo : Philippe Barbosa


